Understanding Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
By Laburrie Beauty
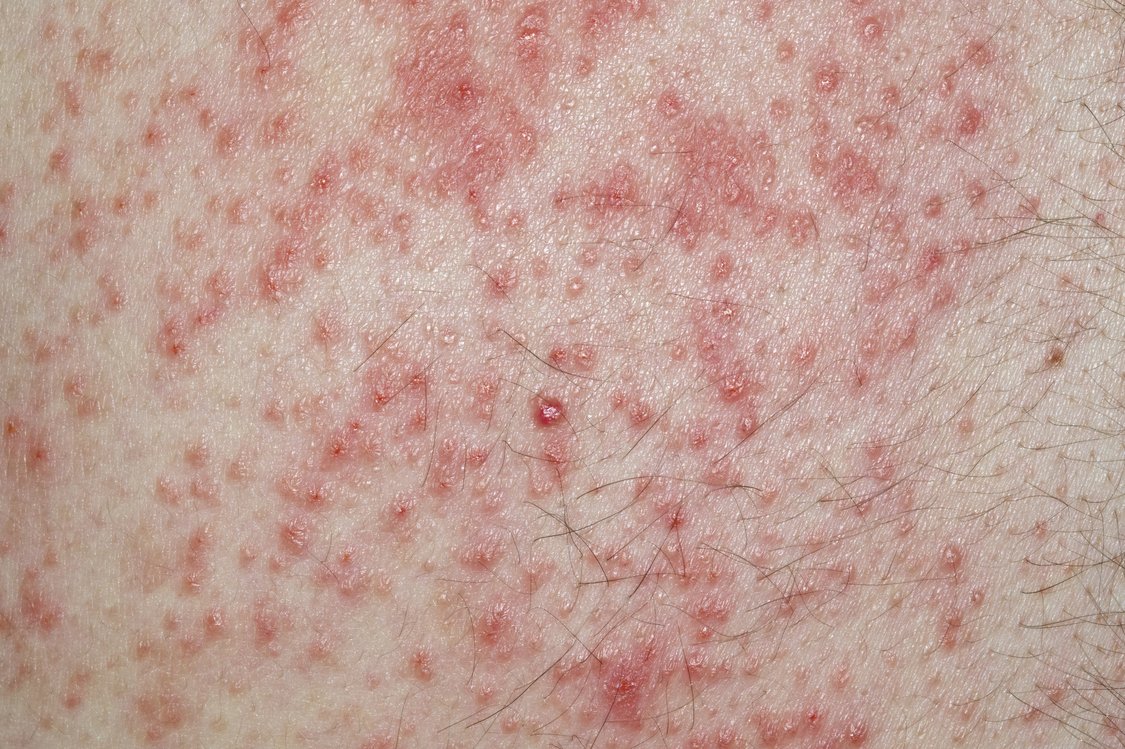
What is Dermatitis?
Dermatitis is a general term that describes inflammation of the skin. It encompasses various conditions, including atopic dermatitis (eczema), contact dermatitis, and seborrheic dermatitis. Symptoms typically include an itchy rash, swollen skin, and redness.
Types of Dermatitis
There are several types of dermatitis, each with different causes and symptoms:
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): A chronic condition characterized by dry, itchy skin and rashes, often occurring in families with a history of allergies or asthma.
- Contact Dermatitis: Occurs when the skin reacts to contact with a particular substance, causing a red, itchy rash. It can be either irritant or allergic contact dermatitis.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Causes scaly patches, red skin, and stubborn dandruff. It affects oily areas of the body, such as the face, sides of the nose, eyebrows, ears, eyelids, and chest.
Causes of Dermatitis
The causes of dermatitis vary depending on the type:
- Atopic Dermatitis: Genetics, immune system dysfunction, and environmental factors can all play a role.
- Contact Dermatitis: Direct contact with an irritant or allergen, such as soap, cosmetics, fragrances, jewelry, or plants like poison ivy.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: The exact cause is unknown, but factors like yeast that lives on the skin, stress, and cold, dry weather can contribute.
Symptoms of Dermatitis
Common symptoms of dermatitis include:
- Red, Itchy Skin: The affected area can be intensely itchy and red.
- Swelling: The skin may become swollen and tender.
- Blisters: In some cases, blisters may form and ooze fluid.
- Cracking and Peeling: Chronic dermatitis can cause the skin to crack and peel.
- Scaly Patches: Especially in seborrheic dermatitis, the skin may become scaly.
Treatment Options
Treatment for dermatitis depends on the type and severity of the condition. Common options include:
- Moisturizers: Regular use of emollients helps to keep the skin hydrated.
- Topical Steroids: Creams and ointments that reduce inflammation and itching.
- Antihistamines: Oral medications that can help relieve itching.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications that control immune system activity for severe cases.
- Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light to reduce symptoms.
"Effective management of dermatitis involves a combination of skincare, avoidance of triggers, and appropriate medical treatments." - Dr. Jane Smith, Dermatologist
Prevention Tips
Preventing dermatitis flare-ups involves good skincare practices and avoiding known triggers:
- Use gentle, fragrance-free skin care products.
- Avoid known irritants and allergens.
- Keep the skin moisturized to prevent dryness.
- Wear protective clothing and gloves when handling irritants.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques.
- Use a humidifier in dry environments to keep the skin hydrated.
